Jim Collins & the Hedgehog Concept
Jim Collins is a student and teacher of what makes great companies tick, and a Socratic advisor to leaders in the business and social sectors. Having invested more than a quarter century in rigorous research, he has authored or coauthored six books that have sold in total more than 10 million copies worldwide. They include Good to Great, the #1 bestseller, which examines why some companies make the leap to superior results, along with its companion work Good to Great and the Social Sectors; the enduring classic Built to Last, which explores how some leaders build companies that remain visionary for generations; How the Mighty Fall, which delves into how once-great companies can self-destruct; and Great by Choice, which is about thriving in chaos—why some do, and others don’t.
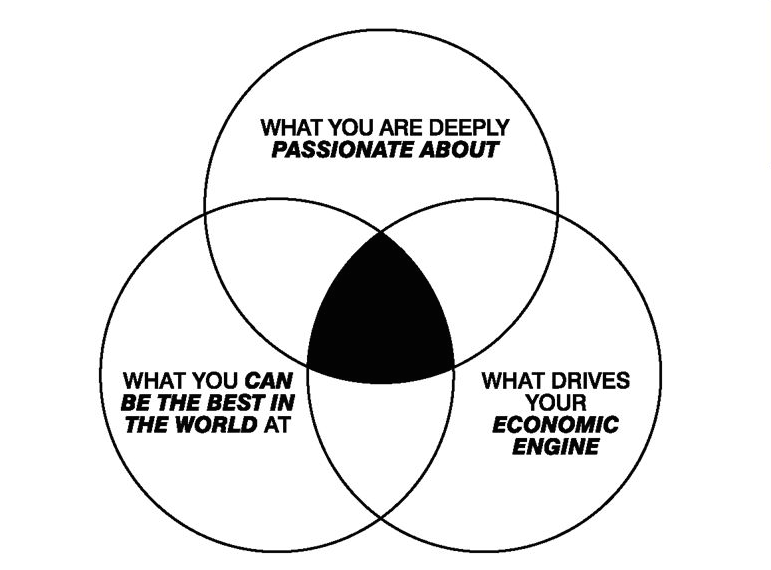
The Hedgehog Concept is developed in the book Good to Great. A simple, crystalline concept that flows from deep understanding about the intersection of three circles: 1) what you are deeply passionate about, 2) what you can be the best in the world at, and 3) what best drives your economic or resource engine. Transformations from good to great come about by a series of good decisions made consistently with a Hedgehog Concept, supremely well executed, accumulating one upon another, over a long period of time.
Are you a hedgehog or a fox? In his famous essay “The Hedgehog and the Fox,” Isaiah Berlin divided the world into hedgehogs and foxes, based upon an ancient Greek parable: “The fox knows many things, but the hedgehog knows one big thing.”
Those who built the good-to-great companies were, to one degree or another, hedgehogs. They used their hedgehog nature to drive toward what we came to call a Hedgehog Concept for their companies. Those who led the comparison companies tended to be foxes, never gaining the clarifying advantage of a Hedgehog Concept, being instead scattered, diffused, and inconsistent.
For the comparison companies, the exact same world that had become so simple and clear to the good-to-great companies remained complex and shrouded in mist. Why? For two reasons. First, the comparison companies never asked the right questions, the questions prompted by the three circles. Second, they set their goals and strategies more from bravado than from understanding.
A Hedgehog Concept is not a goal to be the best, a strategy to be the best, an intention to be the best, a plan to be the best. It is an understanding of what you can be the best at. The distinction is absolutely crucial
Every company would like to be the best at something, but few actually understand—with piercing insight and egoless clarity—what they actually have the potential to be the best at and, just as important, what they cannotbe the best at. And it is this distinction that stands as one of the primary contrasts between the good-to-great companies and the comparison companies.
To go from good to great requires transcending the curse of competence. It requires the discipline to say, “Just because we are good at it—just because we’re making money and generating growth—doesn’t necessarily mean we can become the best at it.” The good-to-great companies understood that doing what you are good at will only make you good; focusing solely on what you can potentially do better than any other organization is the only path to greatness.
As you search for your own concept, keep in mind that when the good-to-great companies finally grasped their Hedgehog Concept, it had none of the tiresome, irritating blasts of mindless bravado typical of the comparison companies. “Yep, we could be the best at that” was stated as the recognition of a fact, no more startling than observing that the sky is blue or the grass is green. When you get your Hedgehog Concept right, it has the quiet ping of truth, like a single, clear, perfectly struck note hanging in the air in the hushed silence of a full auditorium at the end of a quiet movement of a Mozart piano concerto. There is no need to say much of anything; the quiet truth speaks for itself.


